What is UX (User Experience)?
According to ISO 9241-210, user experience is defined as “a person’s perceptions and responses that result from the use or anticipated use of a product, system or service”. User experience includes all the users’ emotions, beliefs, preferences, perceptions, physical and psychological responses, behaviors and accomplishments that occur before, during and after use.
For a service provider or product maker, one of the key success factors of their product design is “to understand what users like and how users like their product and design”. The more they know about their users, the better the product they make. It’s important to understand how users feel about your product or design. There are three factors that could impact users’ experiences: Eyes (Perception of Message), Brain (Logical Reasoning) and Hands (Operation). When we try to dig into a user’s mind, a “usability test” could address all three aspects of user experience.
An increase in product usability can bring positive impacts, such as:
- Increases user productivity
- Increases user satisfaction
- Reduces company training and support costs
- Reduces company development time and costs
- Reduces company maintenance costs
- Increases company sales and revenues
How to design a compelling UX product?
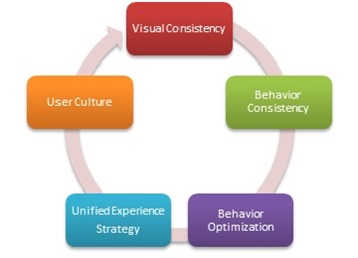
Generally, good user experience reflects a User-Centered Design (UCD). Most of the designs start from the concept of “Principle Bases” then moves on to the concept of “User Centered Design”. From Figure 1, we can see that there are five stages in the the design process.
Figure 1
Visual Consistency & Simplification
In this stage, the design architecture (layout, colors, and styles) should be the focus. When a company designs a product, too many different styles of design can confuse users and even potentially disappoint or frustrate customers.
Behavior Consistency
A product should be consistent in the way it behaves, which makes it easier for the user to learn how to use the product.
Behavior Optimization
After the first two stages, the focus should be placed on how to simplify a pattern for behavior optimization. This makes user actions easier and more powerful.
Unified Experience Strategy
More and more product designs are for communication and idea sharing. Success in product designs isn’t measured by how well they perform a task, but how it works within a complex ecosystem of people, data, devices, and services.
User Culture
The ultimate goal for product design is to change user behavior and to create a new user culture.
All these strategies and scenarios can only help a company plan a product well, but cannot guarantee a popular product. To understand how users like your design at early development stage would be an important check point. Users’ usability test is one of the methods that helps understand what works, what doesn’t work and why it doesn’t work to the product design.
Steps to arrange a good Usability Test
Step 1. Setup Test Goals and Test Plans
Usability testing is a research tool, with its roots in classical experimental methodology. The range of tests one can conduct is considerable, from true classical experiments with large sample sizes and complex test designs, to informal qualitative studies with only a single participant. Each testing approach has different objective, as well as different time and resource requirements.
Step 2. Design the tasks and Questionnaires for the observation
Allion believes a “Scenario-based” test design could lead to a good usability test result. One test scenario comprises several tasks. Task-design is based on the real situation in which users would conceivably perform using a product. The closer the scenarios could reflect reality, the more reliable the test results would be. In addition, the participants will find it easier to “stay in role”.
Once the scenarios and tasks are completely designed, we will also need to design “Questionnaires” for participants to feedback their observation and feeling when performing the designed tasks. With the questionnaire, we will be able to gather preference information from the participants in order to clarify and deepen our understanding of the product’s strengths and weaknesses.
Step 3. Select target user segments (Region, Gender, Age, Power or Amateur User..etc.)
Selecting participants involves identifying and describing the relevant behavior, skills, and knowledge of the person(s) who will use your product. This clear description of the selected user background should have been developed in the early stages of the product development.
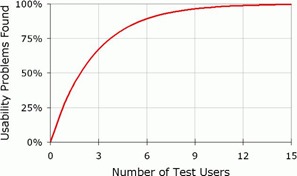
How many participants that we need for the test? According to the research, for usability test, there is no need to find great amount of participants. 6-8 participants per user segment would be sufficient for finding 90% of the problems (Figure 2.).
Figure 2.
Step 4. Perform Pilot Tests to get reference standard
The pilot test is considered an integral part of the test design fine tune. It could address specific test objectives, such as a participant’s first impressions of the task scenarios, related documents and time control. Pilot tests allow participants to get themselves involved into a specific scenario more, or make product makers establish a more fluent process of the formal test.
Step 5. Implement the Test with participant and moderator
The moderator would observe the whole process in which the participants participate in and complete designed tasks. Then, the moderator conducts an interviewing with the participants.
Step 6. Analysis the collected information and feedbacks
Compile and summarize data into recommendations and produce a final report.
Case Study – UX Test and Analysis on Smart Watches
A good UX Test (User Experience Test) should help company discover the potential risks that might degrade users’ preference of their products. Besides the usability test, a comparative test and an analysis of competitor’s products are also practical ways to handle who is using their product and competitor’s products as well. This can be a wonderful source of information to establish the user background for product design.
Allion has successfully conducted usability tests on various products for several years. For example, at the end of 2013, we selected three different types of smart watches, the popular consumer products in post PC era and evaluated their performances. This test report mainly focused on the appearance, UI (User Interface) and the functionality of products. For more information about the report, please refer to the link: New Friend on Wrist: Smart Watch Test Report
Figure 3. DUTs from left to the right: SONY Smart Watch 2, Martian Passport Watch, Pebble Smart Watch
Through usability test and competitive analysis, Allion strengthened on the strengths and weaknesses of each product, gave suggestive feedbacks and provided an insight of smart watch trends. Allion has being devoted to the User Experience test research, helping our valuable customers develop a better product in the market.