Allion Labs
Many people have heard of quality management, but did you know that in manufacturing, quality management is actually divided into two parts, quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC)? How does a factory distinguish between QA and QC? What is the difference in practice? Allion, as a trusted brand of the top tech brands, has accumulated many years of experience in QA and QC when it comes to production lines. Allion is pleased to introduce QA and QC in simple terms and the role it plays in the factory with this article.
What is Quality Assurance (QA)?
QA uses a systematic quality management mechanism to comprehensively ensure external and internal and external work processes in line with standard specifications and procedures to ensure product quality. External work processes include suppliers, third-party manufacturers, and customers, while internal work processes include new product design, research and development, manufacturing, shipment to after-sales service.
Common job categories include:
- Quality Engineer (QE)
Responsible for product QA - Client Quality Engineer (CQE)
Suppliers hire engineers who check product quality for customers - Supplier Quality Engineer (SQE)
Responsible for supplier evaluation, supplier quality audit, guidance on supplier quality, and feed system control
What is Quality Control (QC)?
QC includes product quality inspection, analysis, and improvement after quality problems are found along with control of non-conforming products. There is a process to ensure that products leave the factory with zero defects, meeting customer’s standards.
The process includes:
- Design Quality Control (DQC)
Design quality inspection of products in the design stage, with the goal of checking key aspects of design quality against a set of standards or specifications. - Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
Quality inspection of incoming materials such as raw materials, components, accessories, and packaging materials, ensuring that supplied parts and components are compliant with the quality standardized by brand owners. - In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
Quality inspections from the input of product materials into production to the completion of final product packaging, which includes audit workstations, prototype Inspections, and random Inspections. - Finish or Final Quality Control (FQC)
Product quality inspection and random inspections after production, assembly, and packaging, including product features, functional test, electricity test, interoperability tests, reliability tests (performance tests and life cycle tests). - Outgoing Quality control (OQC)
Factory product inspection before product leaves factory, with random sampling, packaging labels, products, and peripheral layouts checks.
Roles of QA and QC:
- Work perspective
QA work is aimed at preventing product problems. The factory performs various tasks in accordance with the existing production procedures whilst following the correct methods to achieve quality control goals. QC mainly finds potential problems in semi-finished products/finished products, confirms whether the products meet customer requirements and product SPEC, and monitors the quality of products. - Technical perspective
QC practitioners only need to know how to perform the inspection work against the specifications, find potential problems through inspection methods, and audit subsequent control methods. However, QA practitioners not only need to know where the problem is and the cause of the problem, but also need to know the follow-up solution and how to prevent the problem from recurring. They even provide 8D Report or QC Story to record the improvement process of the problem and follow-up tracking, which is more systematic, that belongs to the work with high professional knowledge and technology. - Goal Perspective
QA aims to meet customer requirements, gain customer trust, carry out institutionalized management in the process of product life cycle, establish enterprise quality management system, formulate corresponding document specifications, leave evidence of operation implementation, and verify that every step of the factory’s activities are carried out according to customer requirements. QC is the operation technology and method adopted to make the product meet the quality requirements. This includes inspection, correction, and feedback. The scope is mainly for the inside of the factory.
Although QA and QC are not the same in terms of work level, technical level, and purpose level, the ultimate purpose is to ensure the quality of products and avoid potential problems on the user side, maintaining the corporate brand image.
In today’s factories, the roles and responsibilities of QA and QC are not so clear. In some companies, the quality control engineer must be concurrently responsible for both QC and QA work. Therefore, in addition to the ability to think independently, a quality control engineer should become an all-around quality assurance engineer by focusing on QC and supplemented by QA, or by focusing on QA and supplementing QC.
Combining QA and QC to create your own customized Quality SOP
As an appointed partner of international brand factories, Allion has accumulated many years of QA and QC experience. During this time, we have developed a QA and QC SOP, which can prepare production line related test fixtures and test equipment according to product characteristics and test items, formulating IQC, IPQC, FQC, OQC audit documents, quality reports (including yield, missing problems, etc.), plan a systematic and flexible quality control SOP, and check and confirm in an all-round way. If there are abnormal problems, you can also immediately hold a meeting with the OEM/ODM factory to review and deal with the problem in order to propose an improvement promotion plan to track the improvement effect.
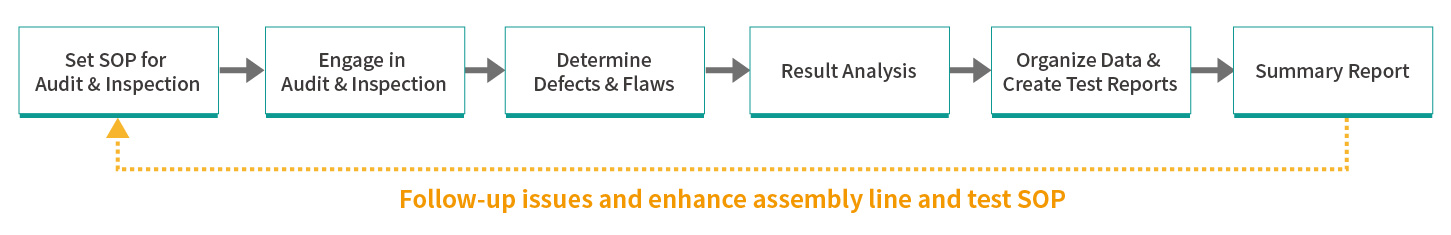
In addition to assisting the QA and QC work of a brand, Allion can also provide corresponding services on the factory side. In order to catch up with the schedule of each development stage, it is necessary to deal with various style problems immediately. The Allion laboratory is equipped with professional equipment and instruments. It can make up for the shortage of factory testing and assist customers in real-time verification to find an issue’s root cause in the shortest time.
Summary
In terms of definition, QA is mainly a case of prior quality assurance work, focusing on prevention which in turn reduces error rates. QC, on the other hand, is the work of quality inspection and expecting to find problems and mistakes within the product before reaching the end-user. QA and QC need to work together in order for the brand to gain internal and external trust.
Allion has many years of experience in assisting brand customers in QA and QC, effectively providing customers with a complete set of quality maintenance testing plans.
We can dispatch senior and well-trained quality engineers (IQC, IPQC, or OQC production line inspection personnel) to cooperate with the manufacturing process of the production line regularly. We also randomly perform quality sampling to inspect and test the condition of the products manufactured at different stages, so as to improve the excellence of the customer’s products.
For more information on quality management, please refer to our Quality Assurance Program or contact us directly at: service@allion.com