The rapid development of smart vehicles has made the digital car key an essential component of modern cars, offering unprecedented convenience to car owners. With digital key technology, there’s no need for traditional physical keys; unlocking, starting the vehicle, and controlling various functions can all be done via a smartphone or wearable device. As the technology becomes more mature, testing and verifying the security of digital keys are becoming increasingly important.
This article delves into the core technologies, application scenarios, risks, and challenges of automotive digital keys, as well as how automated testing can be used for verification.
Core Technologies of Digital Car Keys
Automotive digital keys primarily rely on three core technologies—NFC (Near Field Communication), UWB (Ultra-Wideband), and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)—each with unique characteristics and application scenarios:
NFC (Near Field Communication)
NFC is one of the most commonly used technologies in digital car keys, mainly applied in short-range contactless payment and vehicle unlocking. With a communication range of just a few centimeters, the user must bring the device very close to the vehicle to unlock or start it, providing a high level of security.
UWB (Ultra-Wideband)
UWB technology enables precise positioning over a wider range, allowing for automatic vehicle unlocking. When the car owner approaches the vehicle, UWB can quickly detect and verify their identity, offering a seamless experience without physical contact. This technology not only enhances user convenience but also supports advanced features such as automated parking.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
BLE is primarily used for longer-distance communication, allowing car owners to remotely control vehicle functions, such as starting the engine and adjusting interior temperature, via smartphone. BLE enables digital keys to maintain stable communication without significantly affecting the phone’s battery life.
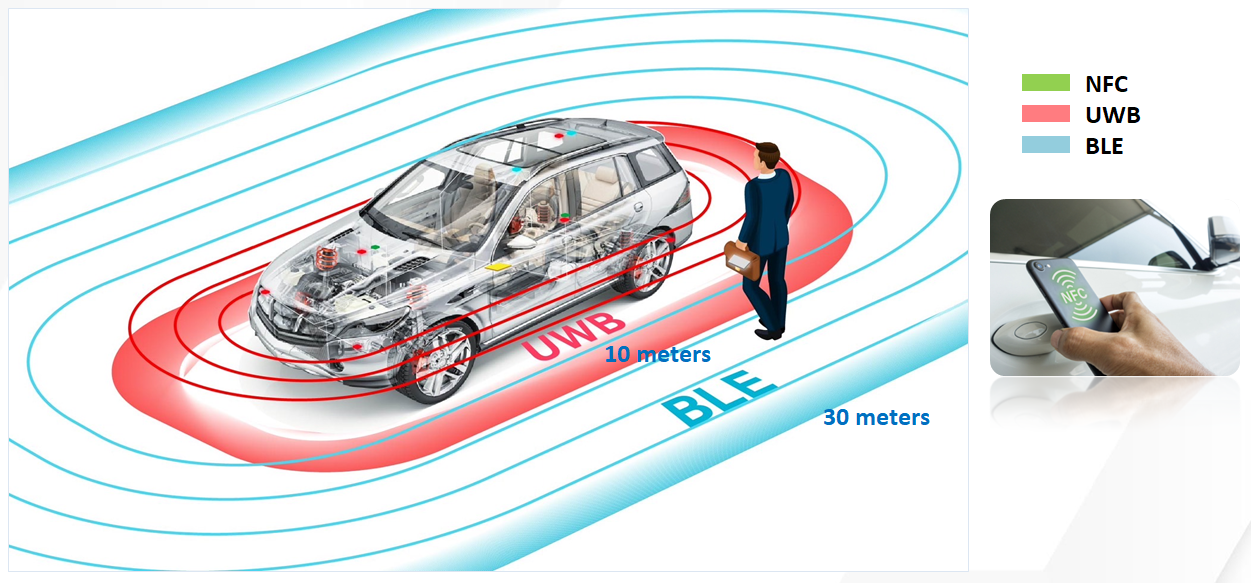
Practical Application Scenarios and Potential Risks of Digital Car Keys
From everyday unlocking and starting to more complex remote control and sharing of the digital key with other users, the application scope of digital keys is expanding. Below are some common application scenarios:

Personalized Unlocking Settings: Digital keys can automatically adjust the seat position, mirror angle, and air conditioning settings based on the user’s preferences, providing a more personalized driving experience.
Digital Key Sharing: Users can share the digital key with others, either temporarily or permanently, via an app, making it convenient for family members or friends to use the vehicle.
Vehicle Location Tracking: When the car owner forgets where they parked in a large parking lot, the digital key can help locate the vehicle quickly using BLE or UWB technology.
While these features greatly enhance driving convenience, they also bring potential risks. For example, if a smartphone is lost or hacked, the digital key could be compromised, threatening vehicle security. Additionally, issues such as wireless signal interference and compatibility with devices from different brands could impact the functionality of the digital key.

Quality Verification Strategies for Digital Keys
Given the critical role of digital keys in vehicle safety, comprehensive verification testing is essential. Key areas to cover in quality verification testing include:
Range and Performance Testing
Testing the digital key’s functionality at various distances to ensure stable operation within specified ranges, while also evaluating its performance under different angles and environmental conditions.
Security Testing
Testing against man-in-the-middle attacks, signal interception, and emergency measures in case of smartphone loss to ensure the high security of the digital key.
Battery Life and Performance Testing
Assessing the digital key’s response time and stability under various battery conditions to ensure reliable operation, even when the battery is low.
Antenna Performance Testing
Testing the vehicle’s reception antennas for signal strength (RSSI) and sensing distance to meet standards, as vehicle manufacturers may require multiple antennas for precise detection systems.
Interoperability Testing for Mobile Devices
Digital car key technology relies heavily on smartphone applications, making compatibility with different phone models, operating systems, and telecom providers an essential factor. Interoperability testing should include but is not limited to:
- Various Brands and Models: Allion recommends testing at least 50 mainstream smartphone models to cover over 90% of user requirements in the market and ensure seamless integration with digital key technology.
- Operating System Compatibility: Testing compatibility across different versions of iOS and Android, as these are the two major mobile operating systems globally.
- Carrier and Chipset Variability: Differences between telecom providers and phone chipsets across countries could affect the operation of the digital key and should be included in the testing scope.

Automated Testing Solutions
To improve testing efficiency and reduce manual intervention, many automakers and suppliers are adopting automated testing solutions. These solutions not only significantly enhance testing efficiency and reduce human error but also ensure comprehensive and precise test results, enabling companies to launch products faster and with a competitive edge. Automated testing helps developers identify hidden issues more quickly, optimize product design, shorten development cycles, and ultimately accelerate market entry and product competitiveness.
- Examples include using robotic arms with suction cups to hold smartphones and gradually approach the sensing area for digital key functionality and response time testing.
- Functional Testing: Simulating real user scenarios to test basic functions such as unlocking, starting, and personalized settings of the digital key.
- Delay and Response Time Testing: Automated testing systems can precisely measure the delay time between sending commands and executing operations, ensuring compliance with design specifications.
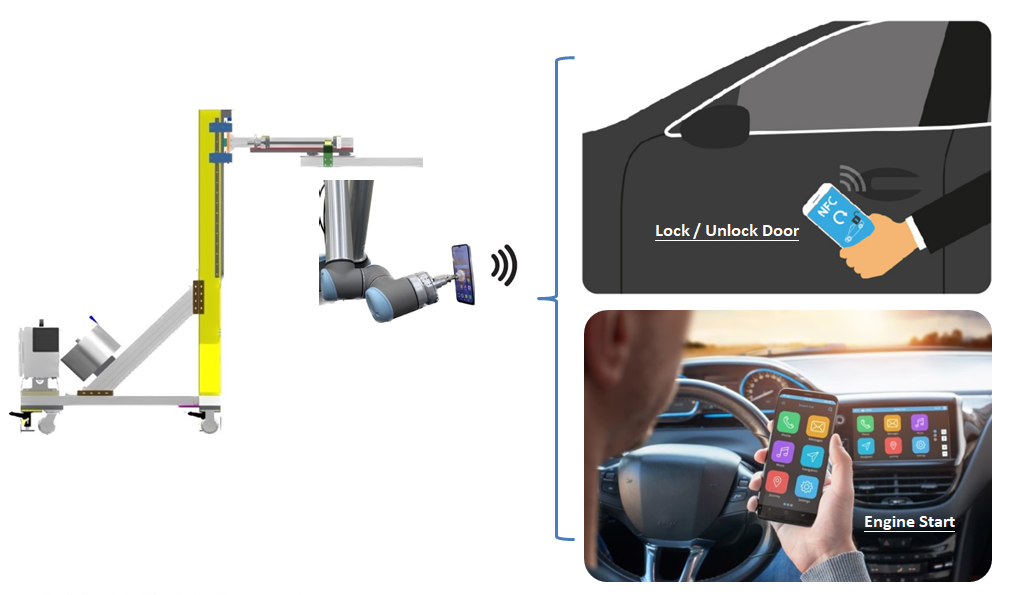
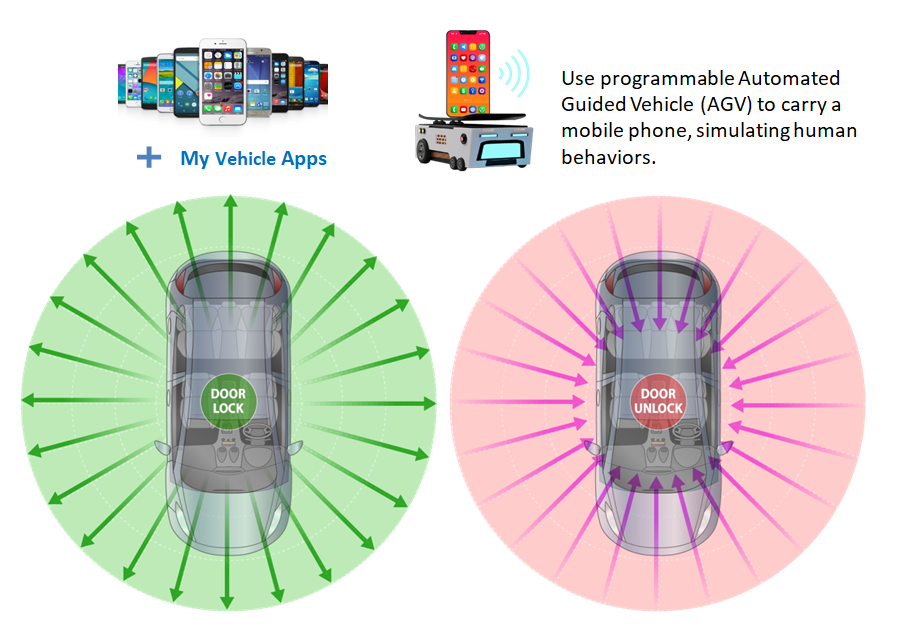
- Application Interoperability Testing: Using programmable Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) equipped with mobile devices to simulate user behavior for large-scale app testing to verify compatibility with digital key hardware and software, ensuring continuity and stability of operation.
Conclusion
The development of digital car key technology brings new opportunities and challenges to the automotive industry. Ensuring security and reliability, while enjoying convenience, is a critical task for all car manufacturers and technology providers. As the technology matures, user expectations for digital keys are constantly rising; they demand ease of use and expect high security features. Only through rigorous verification testing and efficient automated testing solutions can digital key technology meet market expectations and become an indispensable part of the smart vehicle ecosystem.
For any needs related to automotive testing, verification, or consultation services, please feel free to contact us through our online form.The Allion consulting team will sincerely serve you!
Inquiry Form