In-Car Voice Assistant Consulting
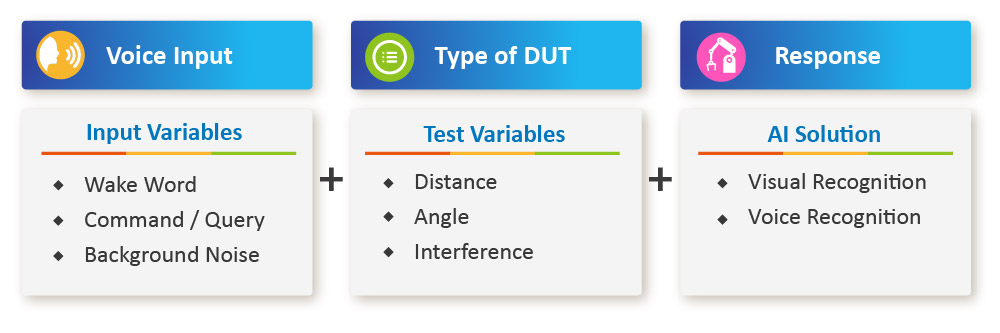
Allion’s AI test platform for in-car voice assistants can monitor and simulate many types of conditions, including distance, angles, interferences, voice profiles, environments, and weather conditions. From product development plan to post launch analysis, Allion helps you improve the accuracy of speech recognition, build voice libraries, process procurement of loudspeakers and microphones, acquire acoustical engineering knowledge, and optimize workforce scheduling.
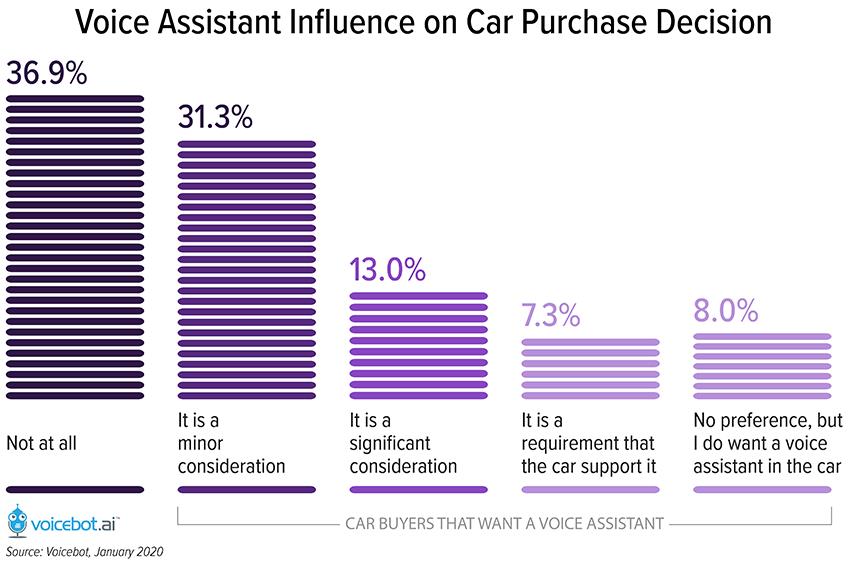
InquiryOver 60% of Car Buyers Agree That Voice Assistant Availability Influences Their Purchase Decisions
According to the report published by Voicebot. ai on January 2020, 63% of drivers consider the presence of an in-car assistant when car-shopping. Moreover, as the automotive technologies continue to advance at a rapid pace, drivers have stronger interests in purchasing cars with the advanced features. This also explains why drivers show clear preferences for cars embedded with voice assistants.
In-car voice assistants now serve as the co-pilot to improve the driving experience. Based on the experience cooperating with automakers, Allion lists the top five user scenarios of in-car voice assistants:
- Make phone calls and receive incoming phone calls
- Voice control navigation
- Send and receive messages
- Play music
- Turn on the radio
How Do In-Car Voice Assistants Work?
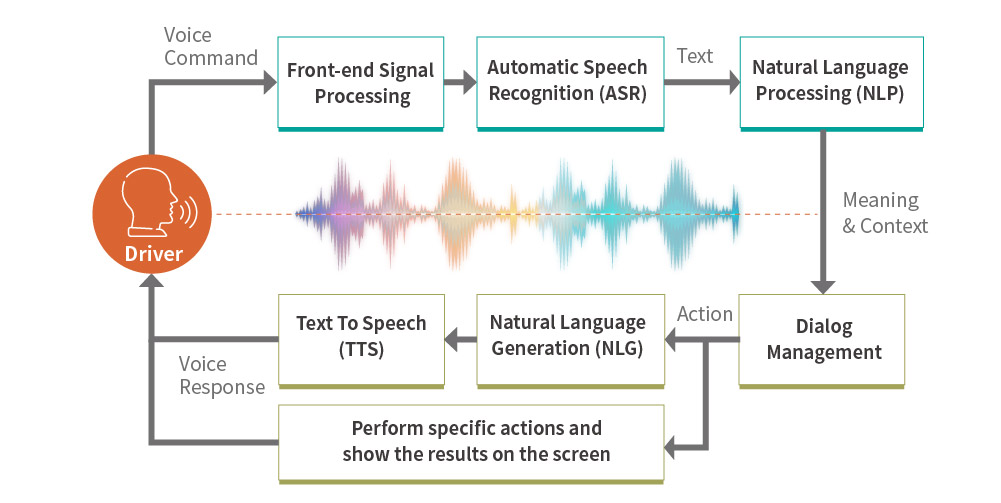
Before responding to users’ commands or questions, in-car voice assistants need to move through three stages: wake words, signal processing and analysis, and dialog management.
Drivers have to activate the in-car voice assistant with wake words. For example, most drivers can access voice-activated features after pressing a button on the steering wheel. Some vehicles support the use of spoken wake words.
(1) Signal Processing: Process sounds and reduce noise impacts in a spoken speech.
(2) Automatic Speech Recognition: Break the spoken speech down into phonemes. Identify words that carry actual meanings.
(3) Natural Language Processing: Use linguistics and algorithms to understand and derive meaning from the spoken speech.
There are two key elements in dialog management. First, it can generate voice feedback. Second, according to users’ voice commands, the dialog manager can further take appropriate actions and show the relevant information on a monitor.
For example, when a user asks for the weather forecast, the corresponding information will be displayed on the head unit monitor.
Here’s another example: If a driver wants to open car windows, the in-car voice assistant will turn the commands into real actions instead of just answering the question.
Why Don’t In-Car Voice Assistants Perform Well?
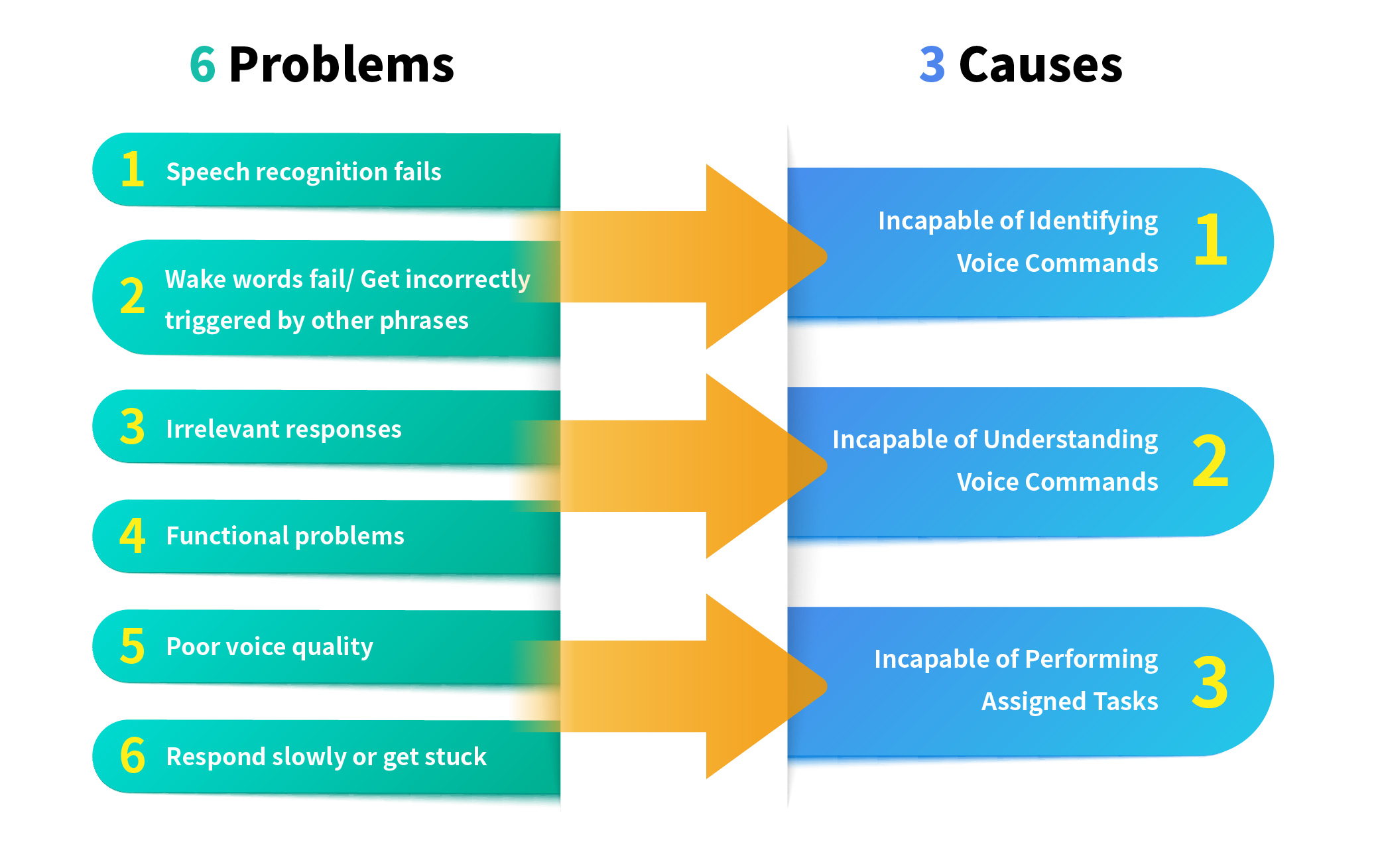
Incapable of Identifying Voice Commands
Since sounds and noises coexist in a vehicle, the vehicle cabin creates a setting where many acoustic scenarios take place. In addition to voice commands given by the driver, there are other types of background noises, such as conversations, music, echoing effects, engine sounds, and tire noises.
Angles and directions from which the voice is projected will also impact the capability of identifying voice commands.
Incapable of Understanding Voice Commands
In-car voice assistants often fail to understand phrases because they only know the commands stored in the pre-defined libraries. If a driver says something other than those pre-defined commands, the AI algorithms will determine the ability to interpret the message.
Here is an example of continuous dialogues.
- Question 1: Do I need an umbrella today?
- In-car voice assistant responds: Yes, you need an umbrella.
- Question 2: How about tomorrow?/ How’s the weather tomorrow?
The in-car voice assistant might not understand the latter one—It assumes that a new question is asked instead of understanding the context as a part of continuous dialogues.
Incapable of Performing Assigned Tasks
In-car voice assistants provide not only answers but also actions. Since they connect with different devices, interoperability and functional issues might arise. For example, when a driver asks to turn on a smart device at home, the in-car voice assistant might not be able to remotely control that device.
If in-car voice assistants do not respond correctly in a short time, the driver will get annoyed, distracted, and even spend more time fixing problems. This causes greater traffic hazards and damages users’ perception of such products.
Advantages of Allion AI Solution for In-Car Voice Assistant Verification
1.High Efficiency—Complex Scenario Simulating
Record car noises to recreate real-life scenarios. Analyze how strong the signal should be to identify voice commands as expected.
More than 12,000 voice commands and different voice profiles (gender/ age/ language/ command/ dialect) are included. The voice data can also be customized.
2.High Accuracy and Consistency—AI-driven Testing and Monitoring
Automatically judge the response provided by the in-car voice assistant.
Accumulate a massive amount of language data and identify the exact cause of defects.
Verify whether the information is accurately shown on the head unit monitor.
Allion as the Expert in Automotive Acoustic Testing
Allion has more than 30 years of testing and certification experiences. We have been working closely with many world-class brands to establish speech recognition standards in the automotive industry. We now offer the Amazon self-test, Cortana self-test, Intel platform voice recognition tests, and other voice assistant verifications. Also, we specialize in acoustic test environment setup, personnel training, technical support, and even post product launch analysis. Allion helps you take care of every single detail in automotive acoustic testing.

- Acoustic Experience—ITU-T / Apple CarPlay / Amazon Alexa
- IoT Application—Interoperability and Compatibility
- In-Car Voice Assistant AI Solution
If you need any assistance, please contact our consulting team or email us at service@allion.com