Allion Labs / Wesley Chen
As networking technology advanced, multimedia content delivery and diversity of smart devices became more viable and as a result, the desire for bandwidth has steadily increased. Most consumers nowadays expect stable and convenient Wi-Fi at home, but may suffer weak wireless signal coverage or unstable wireless connectivity. Some users would setup a wireless repeater to extend the signal coverage, but the repeater should work based on a stable Wi-Fi environment. If users adopt a Wi-Fi extender, the extender may lower Wi-Fi performance by broadcasting Wi-Fi signals.
This imperfect situation may be resolved through the adoption of wired networking technology that piggyback broadband signals over existing power, cable and telephone wires.
What is G.hn
G.hn is an abbreviation of Gigabit Home Networking, a set of wired networking protocols, established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and managed by HGF (HomeGrid Forum). The G.hn protocol allows signal transmission over home power lines, coaxial cables, telephone lines, and even plastic optical fiber for connection speeds up to 1 Gbps. Like wireless technology, G.hn extends Internet connectivity without the need for new wiring. It does not rely on or interfere with existing home networking technology and consumers do not need to replace existing devices. Due to these factors, G.hn seems to be the ultimate wired networking technology, achieving high performance over existing home wiring.
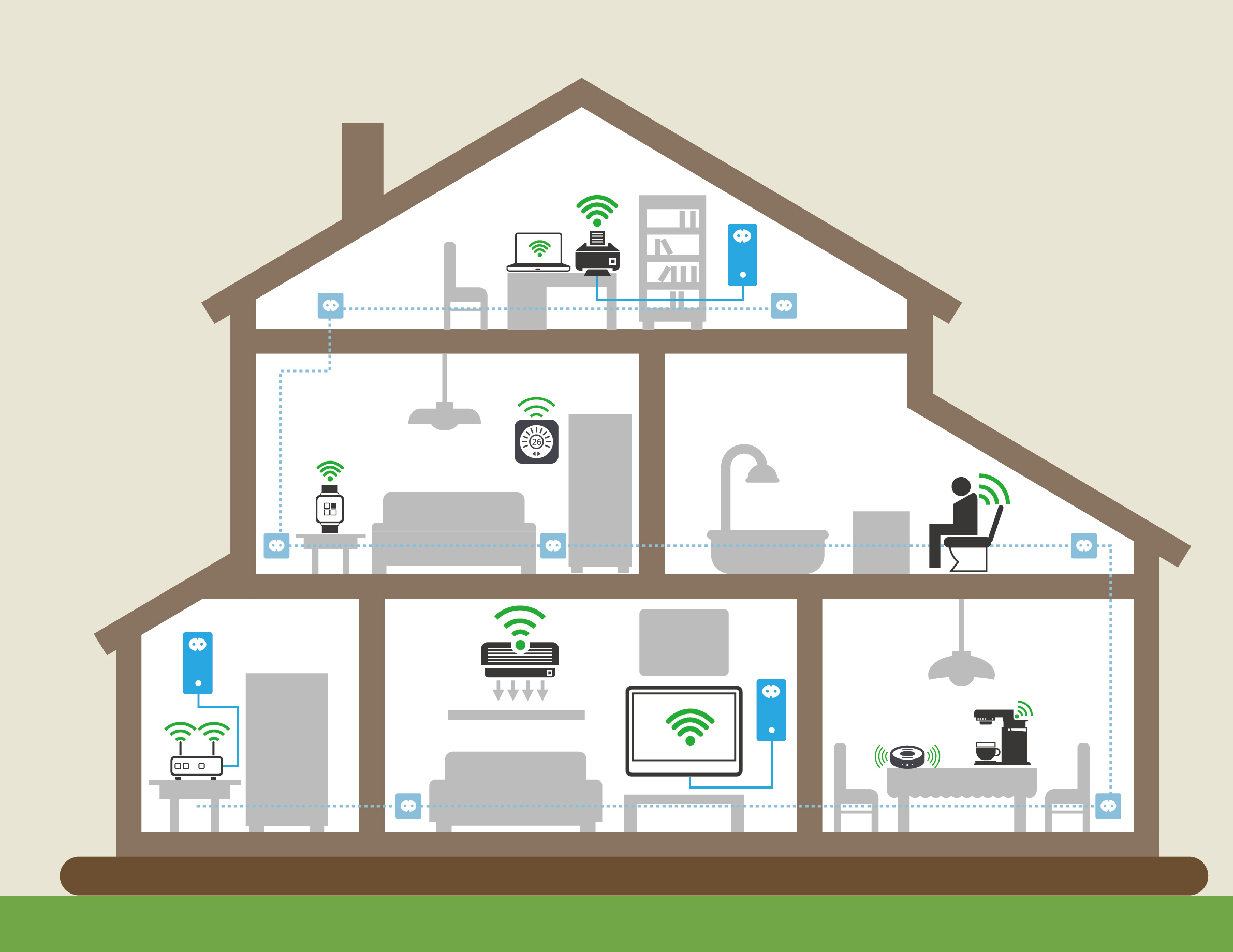
Figure 1: G.hn Home Network Diagram
Powerline Communication Network
Power line connections from the power plant cannot be interrupted between the inside and outside of a home, as electricity must be able to flow freely between the utility and the home residence. Power Line Communication (PLC) networks send signals outside the home that can interfere with other nearby PLC networks. In Asia this occurs frequently with PLC networks, mainly in high-density multi-dwelling unit (MDU) apartments found in major metropolitan areas. G.hn has well-defined algorithms and signaling mechanisms that enable G.hn networks to coexist with other PLC networks.
Power line communication network may be an alternative solution for consumers, but also bring some potential risks. They are:
1. PCL adapters are used in pair. The pairing issues might arise when users are connecting them for the first time.
2.Users might experience signal bleed via unencrypted powerline.
3.Powerline should transmit packet signal but also have noise generated from device connections.
HGF and BBF worked together to develop Performance Test Plan –TR-208 for Broadband Powerline Communication Systems (PLC)
To better control the PLC quality, the HomeGrid Forum and the Broadband Forum are working together to develop the interoperability program for Broadband powerline communication systems (PLC) to verify the adherence to the ITU standard and bring a fast, flexible and reliable communication link between the different devices present at home.
Smart device manufacturers, network communication providers, telecom companies and test labs could bring reliable G.hn solutions to market by following the TR-208. To learn more details about TR-208 Test Plan, please refer to the following URL link: https://www.broadband-forum.org/testing-and-certification-programs/in-home-network-testing
TR-208 Test Coverage and Main Categories of Tests
As the only test house for G.hn certification and validation in the world, Allion will share the keys of TR-208 Test Plan in the following paragraphs:
TR-208 Test Scope
| Category | Family |
| Throughput Performance | Rate vs Attenuation |
| Bidirectional Traffic | |
| Neighbouring Networks | Rate in NN Conditions |
| Admission in NN Conditions | |
| PSD Measurements | Validation of PSD |
| Notches | |
| Noise Immunity | Noise Immunity |
| Topology | Network Setup |
| Relay | |
| Traffic | Latency |
| Bursts | |
| Flow Maintenance | |
| Throughput | |
| Security | Access control |
| P2P Encryption | |
| QoS | QoS |
| Multinode Performance | Multinode Performance |
Table 1: Test Scope
Main Categories of Tests
Here we introduce five key test items and the corresponding test results to help you better understand TR-208 Test Plan quickly.
Test the performance of powerline systems under different conditions of noise, attenuation of the line and electrical infrastructure. Through the competitive analysis, vendors could easily get to know their throughput performance among various G.hn systems. As the Figure 2 shows that System B has better performance than the other ones.
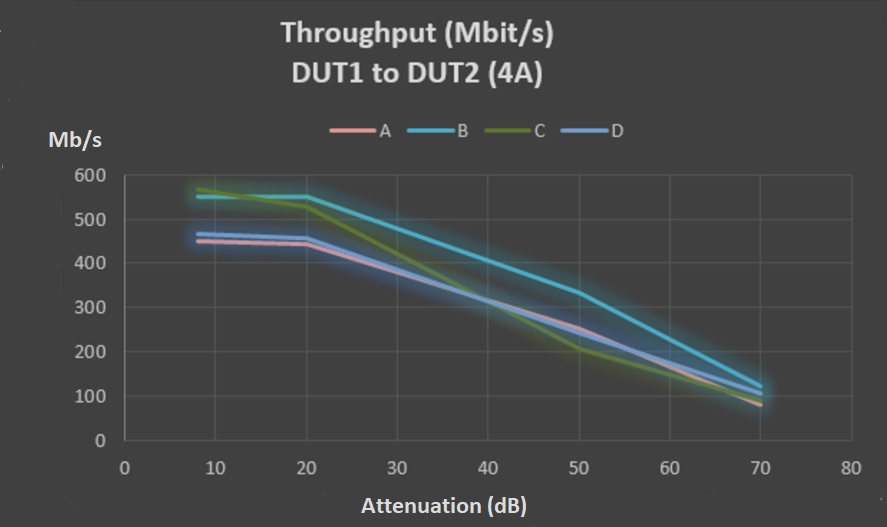
Figure 2: Through Performance Results
The below table (Table 2) shows the requirements of throughput performance defined by G.hn Test Specification. Vendors also have to evaluate whether the testing results achieve performance requirements or not.
| For interface of 1G Base-T | 8dB | 20dB | 50dB | 70dB |
| 100 MHz @ 1518 Bytes | 627 | 627 | 601 | 304 |
| 100 MHz @ 64 Bytes | 285 | 285 | 285 | 251 |
| 50 MHz @ 1518 Bytes | 356 | 357 | 245 | 103 |
| 50 MHz @ 64 Bytes | 190 | 190 | 184 | 95 |
Table 2: G.hn Throughput Limits (Mbits/s)
Readers might not know how strict the testing spec is. Take a real scenario as an example. Even G.hn PLC works under the poor signal level (70 dB attenuation) where wires or loops are connected, the testing requirement of internet speed can still meet the recommended internet speed for Netflix streaming video (see the above the 70 dB column no matter the frame size 1518 Bytes or 64 Bytes.) It means that users may enjoy Ultra HD quality on TV via the G.hn system.
The recommended internet download speed for Netflix content:
- 0.5 Megabits per second – Required broadband connection speed
- 1.5 Megabits per second – Recommended broadband connection speed
- 3.0 Megabits per second – Recommended for SD quality
- 5.0 Megabits per second – Recommended for HD quality
- 25 Megabits per second – Recommended for Ultra HD quality
Test the behavior of the powerline system in presence of a neighboring network of the same technology (e.g. intranet for employees and extranet for guests both exists)under different attenuation conditions.
Measure transmit PSD in-band and out of band for the system under test. If power out (dBm) is much higher than the ITU-T standard, it will easily cause safety issues.
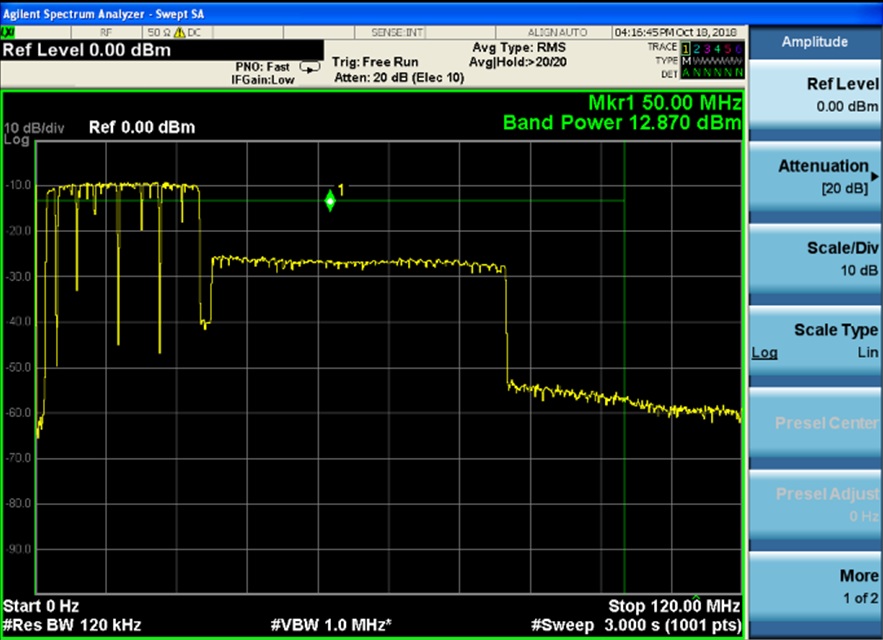
Figure 3: PSD Measurement Result
Test the capacity of the system to handle different traffic types and maintaining the QoS of that traffic.
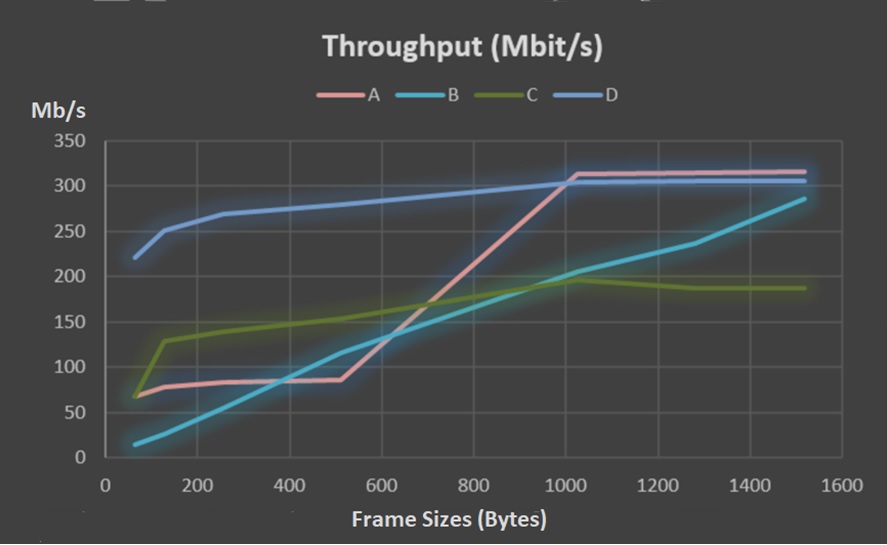
Figure 4: Traffic Test Results
Test the capacity of the system to operate in a network with multiple active nodes.
TR-208 and TR-398 to ensure performance for PLC products
The above is all about TR-208. Except TR-208 testing service, Allion Labs is also capable of TR-398 testing service. TR-398 is a testing standard which is currently launched by Broadband Forum and designed for measuring Wi-Fi performances. By following the TR-398 testing and TR-208 testing standard, vendors could ensure PLC products and also the overall Wi-Fi performance of PLC Wi-Fi Extender.
Allion is your best solution partner to provide PLC testing services.