In recent years, NVMe SSDs can be seen in desktop PCs, laptops, and new servers. The question is, how are NVMe SSDs different from previous types of SSDs?
A Non-volatile Memory (NVMe) SSD is an SSD based on PCIe. Data is accessed through the non-volatile memory attached to the PCIe bus. It’s a new type of solid-state transmission protocol different from previous generation SSDs/ The biggest difference is the transmission interface. The NVMe protocol is specifically designed for SSDs compared with the SATA protocol, which was developed for HDDs. Using SATA for SSDs would be like handicapping a high-speed low-latency device. NVMe SSDs have significantly improved speeds of 7.88GB/s for Gen4 x4 Lane, as opposed to SATA 6G which has a speed of 600MB/s.
NVMe also effectively reduces latency. The native PCIe master directly connects to the CPI instead of the traditional SATA connection, which connects to the southbridge and then to the CPU. In terms of appearance, NVMe SSDs support M.2 interfaces, which are significantly smaller than the early 2.5-inch SSD SATA interface, allowing laptops to become thinner and lighter.
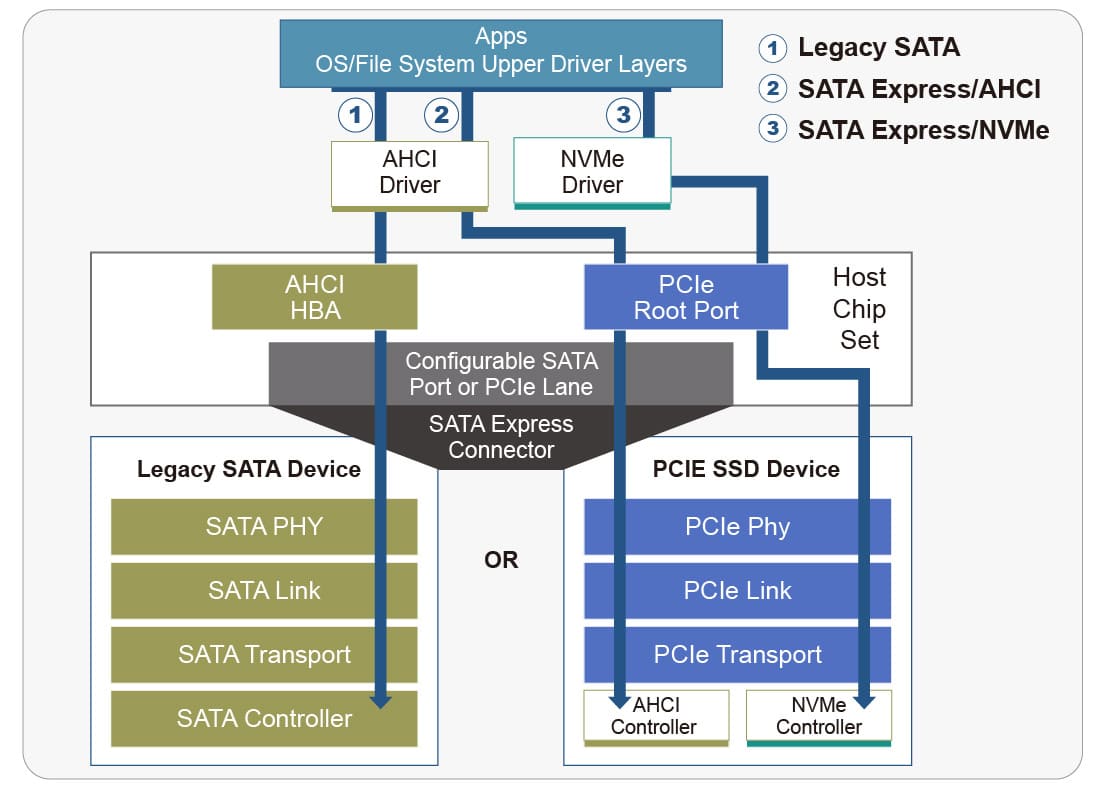
As NVMe SSDs gradually become mainstream, how can manufacturers seize this market opportunity? An NVMe SSD must be sent out for various verification tests in addition to internal testing. The most direct method to verify an NVMe SSD product is with a Protocol Test and a Regression Test. Allion has partnered with Ulink, a well-known verification testing equipment developer, and utilized their tools to conduct tests for NVMe SSDs. So, what is the protocol test and regression test? Here is a simple explanation.
NVMe Protocol Test
To verify whether the NVMe SSD complies with the NVM Express 1.3d specifications, a protocol test is conducted to run a functional check on the controller and confirm the compliance of the return value. Protocol Test items:
- Abort
- Create/Delete IO Queue
- Async Event Request
- Device Self Test
- Sanitize
- Controller Capabilities
- Identify
- Get Log
- Get/Set Feature
- Compare
- Flush
- Read, Write, Write Uncorrectable, Write Zero
- Power States
- Data Set Management
- Firmware Download
- Format NVM
- NVM Resets
NVMe Regression test
After confirming the protocol test, the next steps are to verify the data read and write, whether the SSD can activate the protection mechanism during an unexpected power outage, and conduct stress testing defined by JEDEC (JEDEC 219A). These steps can ensure data accuracy after reading and writing data for long periods. Regression Test items:
- Power Cycle with Random commands
- Power Cycle with Data compare
- MD5 with power cycle
- JEDEC Workload Client/Enterprise
Other than these two tests, we can also analyze the results of tests for products that did not pass verification testing and help clients solve their issues. Allion believes that with these two tests, products can last in the market and provide consumers with a sense of trust.
Not only are the protocol tests and regression tests required for modern SSD products, but reliability testing is also crucial for quality control. Allion, a professional testing laboratory with a complete range of testing equipment and testing environments, can provide tests such as thermal testing and voltage testing to verify the product reliability of these products. We can customize testing conditions and provide SNIA client/enterprise tests to analyze SSD performance. Allion, a testing laboratory that has been established in this industry for decades, can provide comprehensive in-depth testing services for clients.
If you have any further needs for testing, verification, or consulting services related to the server ecosystem, please feel free to explore the following services online or contact us through the online form.