Allion Labs / Tina Yu
8K TV has been a trending topic ever since Japan announced 8K broadcast plans for Tokyo 2020 Olympics. At CES 2020, TV manufacturers such as SONY, Sharp, LG, Samsung, and TCL all showed off their own 8K models. According to IHS Markit report, 8K TV shipments were less than 20,000 units in 2018, but the shipments would reach 430,000 units in 2019. By 2020, it is estimated to approach 2 million units. The statistics show that 8K TV can be one of the most profitable businesses in the foreseeable future.
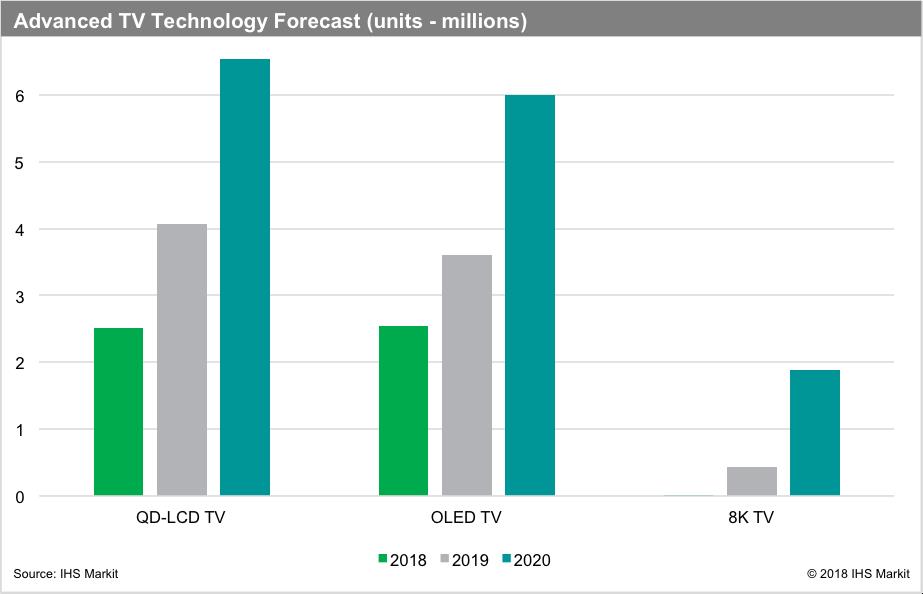 Statistics from IHS Markit
Statistics from IHS Markit
Currently, 4K is the dominant standard in the market. You can buy a 4K TV at a price lower than US$ 630. For most TVs, HDMI port is one of the most indispensable interfaces.
At the end of 2017, HDMI Licensing Administrator (HDMI LA) licensed HDMI 2.1, which is the most recent update of the HDMI specification. The biggest highlight of HDMI 2.1 is the bandwidth capability is increased up to 48Gbps. This makes higher refresh rates including 8K60 and resolutions up to 10K possible. Therefore, the age of 8K is on the horizon and 8K will speed up the elimination of 4K.

![]()
Many challenges are ahead for 8K to become the dominant standard
Although there’s not much difference between the interface and pin configurations of HDMI 2.1 and that of HDMI 2.0, HDMI 2.1 8K and HDMI 2.0 4K are two different types of technologies. HDMI 2.1 specification is more stringent and complex than the previous version.
The following table shows the difference between the two HDMI specifications:
| Signal | HDMI 2.0 | HDMI 2.1 |
| Max Bandwidth | 18Gbps | 48Gbps |
| Transmission | TMDS | FRL |
| AV Channel | D0, D1, D2 | L0, L1, L2, L3 |
| Coding | 8b/10b | 16b/18b |
| Compression | – | DSC 1.2 |
| Compatible with previous versions | Yes
(HDMI 1.4b) |
Yes
(HDMI 1.4b, HDMI 2.0) |
HDMI 2.1 has a maximum bandwidth of 48Gbps, about 2.6 times faster than HDMI 2.0. The previous TMDS technology and the coding method of 8b/10b are no longer enough for HDMI 2.1. Why? Let’s take a look at what TMDS means.
- TMDS stands for Transition Minimized Differential Signaling. Developed by Silicon Image in the US, TMDS is a technology for transmitting high-speed data.
- TMDS was first used on the DVI interface and later on HDMI.
- TMDS electrically transmits information by using two pins as differential signals.
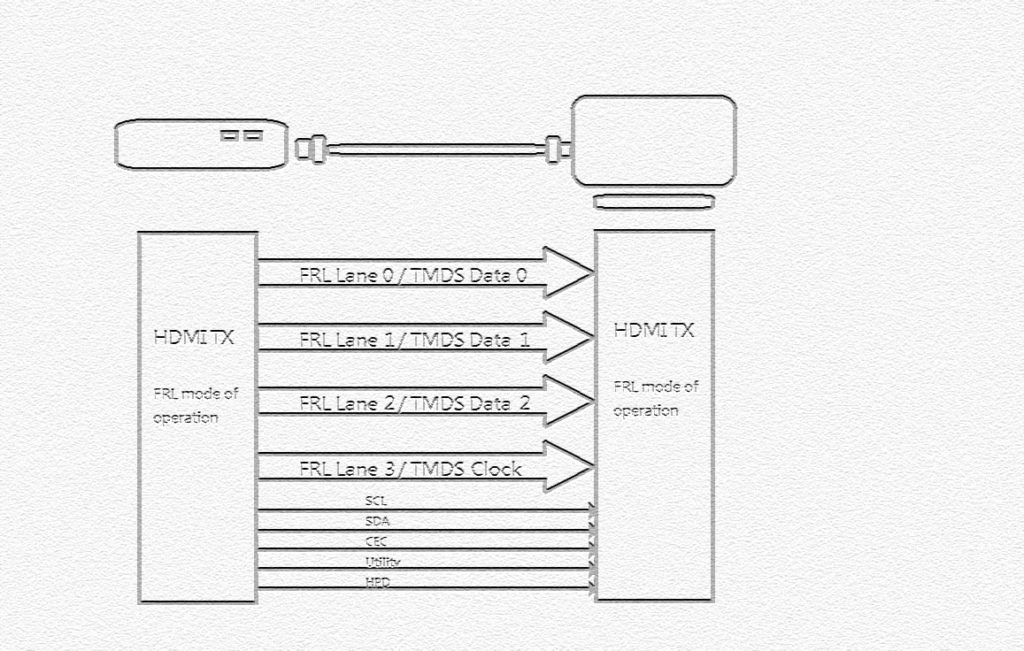
- TMDS transmits video signals via four pairs TMDS channel (Clock, Data0, Data1, Data2).
- The receiver uses the TMDS clock as a frequency reference for data recovery. The A/V signal is processed by the other three pairs of TMDS data channels.
- 8b/10b is an encoding method that converts 8-bit input signals into 10-bit codes. The main purpose of 8b/10b is to reduce EMI and improve the signal transmission rate via differential signaling.
Based on the above-mentioned TMDS features, we conclude that adding a new data channel is not the best way to increase the bandwidth. In other words, we could transfer higher amount of data in the existing data channels. However, both ways are far from perfect. That’s why Fixed Rate Link (FRL) transmission technology and the 16b/18b encoding method came into being. FRL features are listed as follows:
- As its name suggests, FRL means Fixed Rate of Bandwidth.
- FRL Lane 0, Lane 1, Lane 2, and Lane 3 correspond to TMDS Clock, Data 0, Data 1, Data 2.
- Instead of using three pairs of channels, FRL uses four pairs of lanes to transfer data because FRL does not require a clock channel like TMDS does.
- The coding of 8b/10b becomes 16b/18b and the coding efficiency increases by 9%.
- FRL adopts VESA DSC compression technology and supports up to 10K resolution at 120Hz.
- The transmission mode of AC-coupled FRL has replaced the DC-coupled TMDS.
- FRL Link Training is compatible with TMDS mode.
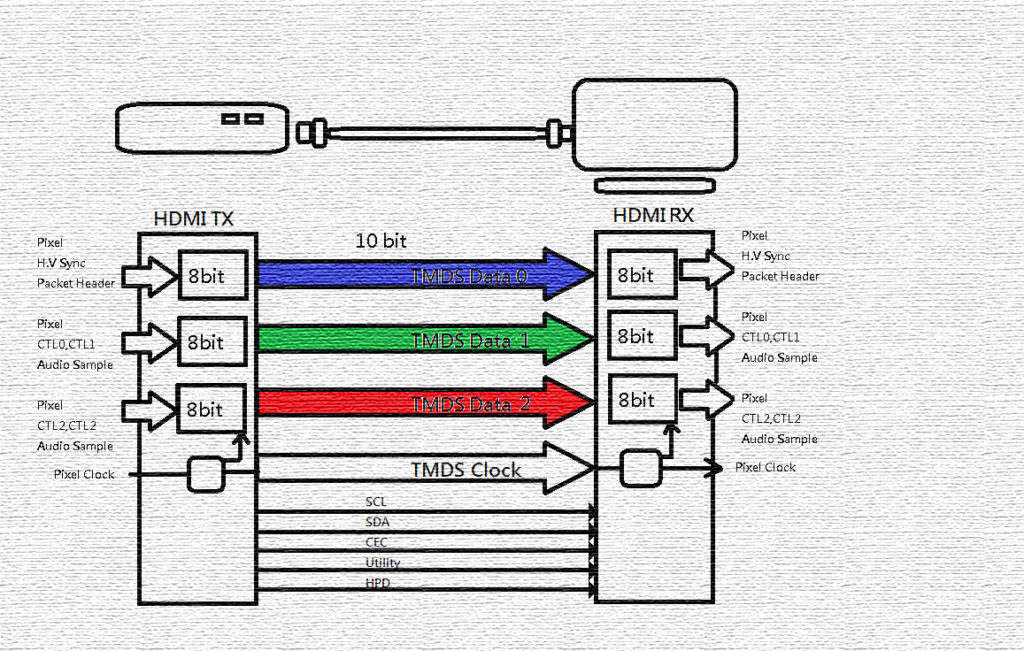
For manufacturers and developers, it is challenging to meet the new FRL mode while remaining compatible with the original TMDS mode.
Allion 8K Test Solution
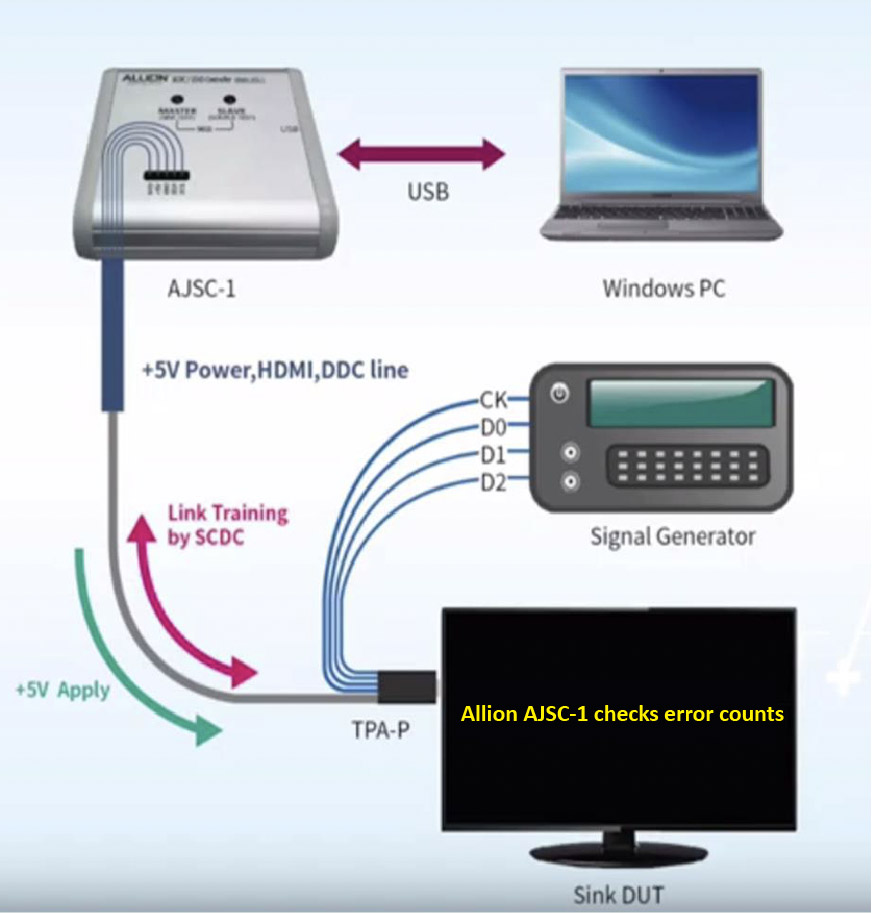
In order to speed up the HDMI 2.1 compliance process for our clients, Allion has developed the SCDC controller (Allion AJSC-1), which is used for the 8K electrical compliance testing. Test plans are listed as follows:
- 8K Verification Test
- FRL Electrical Test
- FRL Protocol Test
- 8K Video Test
- HDMI 2.0 Compliance Test
- TMDS Electrical Test
- TMDS Protocol Test
- TMDS Decoding Test
- TMDS Video Timing Test
- EDID related test
- HDMI 1.4 Compliance Test
- EDID/E-DDC Test
- Electrical Test
- Protocol Test
- Video Test
- Audio Test
- Interoperability with DVI Test
- Advanced Features
Allion Case Study
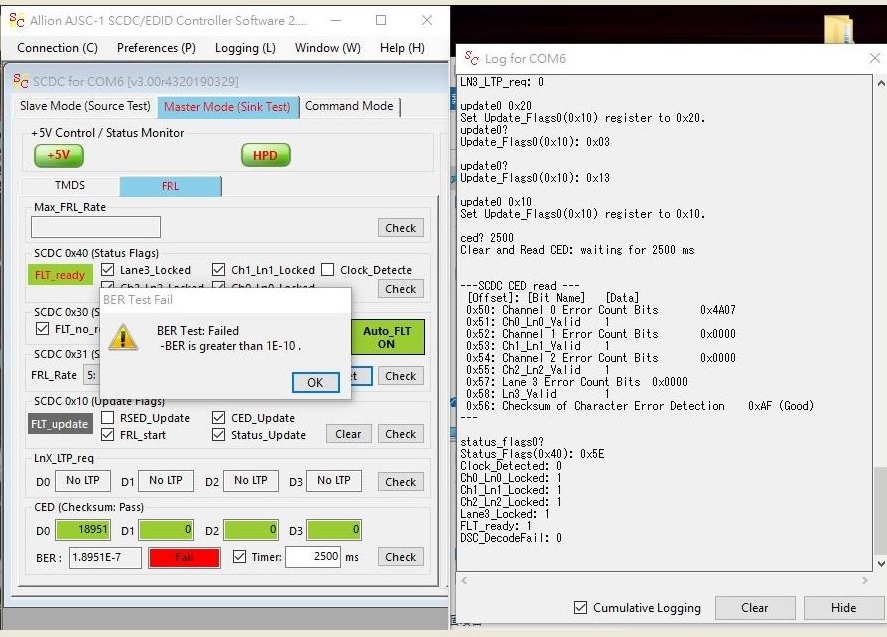
One of the biggest problems with HDMI 2.1 8K TV is that there will be errors when it receives a signal containing jitter. The Debug GUI of Allion AJSC-1 can discover the source of the errors within a short period of time.
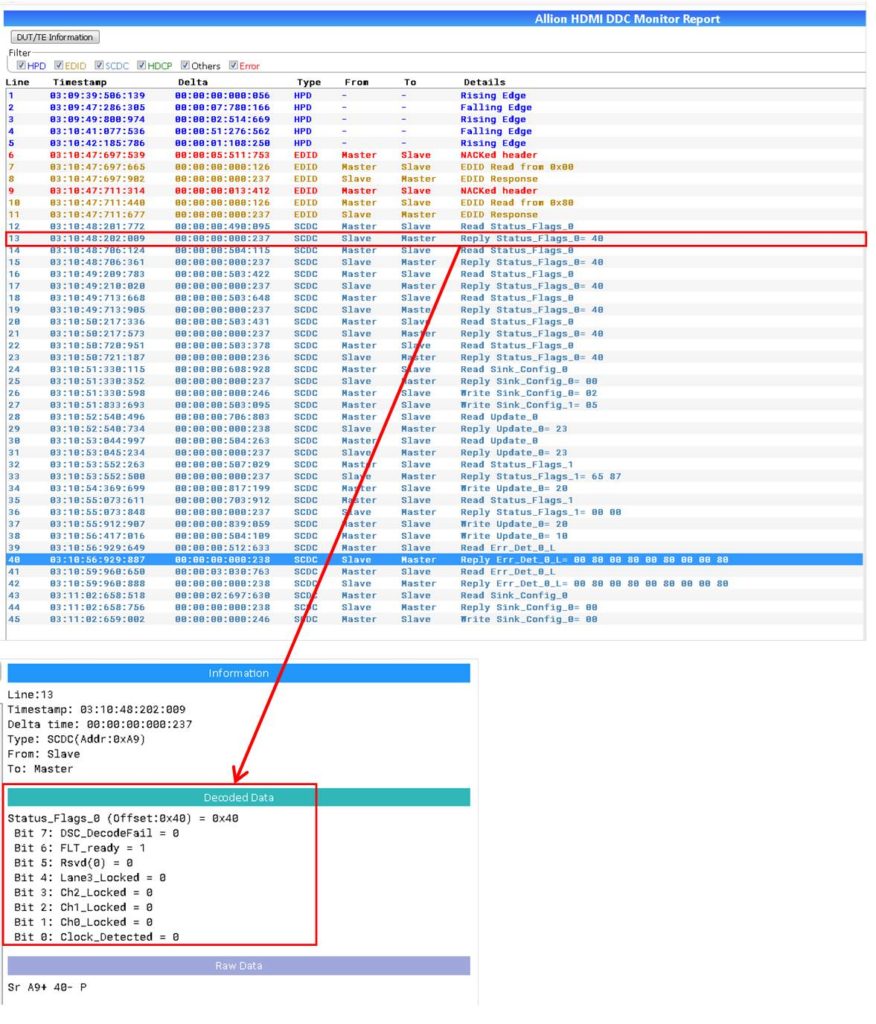
Link Training is also a critical issue. Through another GUI of a DDC Monitor, we can quickly find out whether the relevant Register is compliant with the HDMI 2.1 specification.
As one of the leading test labs in the world, Allion has been working closely with many international associations and has designed test instrument and tools to ensure the quality of HDMI products. For more details about 8K TV and other applications, don’t hesitate to contact us at service@allion.com!